Filología Inglesa
Vocabulary building
Vocabulary building
Affixes and roots
Adding affixes to existing words (the base or root) to form new words is common in academic English. Prefixes are added to the front of the base (like ![]()
dislike), whereas suffixes are added to the end of the base (active ![]()
activate). Prefixes usually do not change the class of the base word, but suffixes usually do change the class of the word.
The most common prefixes used to form new verbs in academic English are: re-, dis-, over-, un-, mis-, out-. The most common suffixes are: -ise, -en, -ate, -(i)fy. By far the most common affix in academic English is -ise.
Verbs
e.g. prefix + verb ![]()
verb
| Prefix | Meaning | Examples |
| re- | again or back | restructure, revisit, reappear, rebuild, refinance |
| dis- | reverses the meaning of the verb | disappear, disallow, disarm, disconnect, discontinue |
| over- | too much | overbook, oversleep, overwork |
| un- | reverses the meaning of the verb | unbend, uncouple, unfasten |
| mis- | badly or wrongly | mislead, misinform, misidentify |
| out- | more or better than others | outperform, outbid |
| be- | make or cause | befriend, belittle |
| co- | together | co-exist, co-operate, co-own |
| de- | do the opposite of | devalue, deselect |
| fore- | earlier, before | foreclose, foresee |
| inter- | between | interact, intermix, interface |
| pre- | before | pre-expose, prejudge, pretest |
| sub- | under/below | subcontract, subdivide |
| trans- | across, over | transform, transcribe, transplant |
| under- | not enough | underfund, undersell, undervalue, underdevelop |
e.g. Suffix used to form verbs with the meaning "cause to be".
| Suffix | Example |
| -ise | stabilise, characterise, symbolise, visualise, specialise |
| -ate | differentiate, liquidate, pollinate, duplicate, fabricate |
| -fy | classify, exemplify, simplify, justify |
| -en | awaken, fasten, shorten, moisten |
Nouns
The most common prefixes used to form new nouns in academic English are: co- and sub-. The most common suffixes are: -tion, -ity, -er, -ness, -ism, -ment, -ant, -ship, -age, -ery. By far the most common noun affix in academic English is -tion.
e.g. prefix + noun 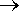
noun
| Prefix | Meaning | Examples |
| anti- | against | anticlimax, antidote, antithesis |
| auto- | self | autobiography, automobile |
| bi- | two | bilingualism, biculturalism, bi-metalism |
| co- | joint | co-founder, co-owner, co-descendant |
| counter- | against | counter-argument, counter-example, counter-proposal |
| dis- | the converse of | discomfort, dislike |
| ex- | former | ex-chairman, ex-hunter |
| hyper- | extreme | hyperinflation, hypersurface |
| in- | the converse of | inattention, incoherence, incompatibility |
| in- | inside | inpatient, |
| inter- | between | interaction, inter-change, interference |
| kilo- | thousand | kilobyte |
| mal- | bad | malfunction, maltreatment, malnutrition |
| mega- | million | megabyte |
| mis- | wrong | misconduct, misdeed, mismanagement |
| mini- | small | mini-publication, mini-theory |
| mono- | one | monosyllable, monograph, monogamy |
| neo- | new | neo-colonialism, neo-impressionism |
| out- | separate | outbuilding, |
| poly- | many | polysyllable |
| pseudo- | false | pseudo-expert |
| re- | again | re-organisation, re-assessment, re-examination |
| semi- | half | semicircle, semi-darkness |
| sub- | below | subset, subdivision |
| super- | more than, above | superset, superimposition, superpowers |
| sur- | over and above | surtax |
| tele- | distant | telecommunications, |
| tri- | three | tripartism |
| ultra- | beyond | ultrasound |
| under- | below, too little | underpayment, under-development, undergraduate |
| vice- | deputy | vice-president |
e.g. Suffix added to a verb (V), noun (N) or adjective (A) 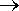
noun
| Suffix | Meaning | Examples |
| -tion | action/instance of V-ing | alteration, demonstration |
| -er | person who V-s | advertiser, driver |
| -ment | action/instance of V-ing | development, punishment, unemployment |
| -ant | person who V-s | assistant, consultant |
| -age | action/result of V | breakage, wastage, package |
| -al | action/result of V | denial, proposal, refusal, dismissal |
| -ence | action/result of V | preference, dependence, interference |
| -ery/-ry | action/instance of V-ing | bribery, robbery, misery |
| Suffix | Meaning | Examples |
| -er | person concerned with N | astronomer, geographer |
| -ism | doctrine of N | Marxism, Maoism, Thatcherism |
| -ship | state of being N | friendship, citizenship, leadership |
| -age | collection of N | baggage, plumage |
| Suffix | Meaning | Examples |
| -ity | state or quality of being A | ability, similarity, responsibility, curiosity |
| -ness | state or quality of being A | darkness, preparedness, consciousness |
| -cy | state or quality of being A | urgency, efficiency, frequency |
Adjectives
Many adjectives are formed from a base of a different class with a suffix (e.g. -less, -ous). Adjectives can also be formed from other adjectives, especially by the negative prefixes (un-, in- and non-).
The most common suffixes are -al, -ent, -ive, -ous, -ful, -less.
e.g. Suffix added to verbs or nouns 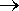
adjective
| Suffix | Example |
| -al | central, political, national, optional, professional |
| -ent | different, dependent, excellent |
| -ive | attractive, effective, imaginative, repetitive |
| -ous | continuous, dangerous, famous |
| -ful | beautiful, peaceful, careful |
| -less | endless, homeless, careless, thoughtless |
| -able | drinkable, countable, avoidable, |
e.g. negative + adjective 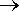
adjective
| Prefix | Examples |
| un- | unfortunate, uncomfortable, unjust |
| im-/in-/ir-/il- | immature, impatient, improbable, inconvenient, irreplaceable, illegal |
| non- | non-fiction, non-political, non-neutral |
| dis- | disloyal, dissimilar, dishonest |
Mixed
e.g. base with both prefix and suffix
Adjectives: uncomfortable, unavoidable, unimaginative, inactive, semi-circular
Nouns: disappointment, misinformation, reformulation
Word formation
Formal written English uses nouns more than verbs. For example, judgement rather than judge, development rather than develop, admiration rather than admire.
There appeared to be evidence of differential treatment of children.
This is reflected in our admiration for people who have made something of their lives, sometimes against great odds, and in our somewhat disappointed judgment of those who merely drift through life.
All airfields in the country would be nationalised, and the government would continue with the development of new aircraft as recommended by the Brabazon Committee.
Associated with nominalisation is the occurrence of prepositional phrases, introduced by of:
judgment of those
treatment of children
development of new aircraft
-tion is the most common suffix used in this way. For example: alteration, resignation.
However others are: -ity ability, similarity, complexity; -ness blindness, darkness, preparedness; -ment development, encouragement; -ship friendship; -age mileage; -ery robbery, bribery; -al arrival; -ance assistance, resemblance.
Descargar
| Enviado por: | Ana Ojeda |
| Idioma: | inglés |
| País: | España |
